Preamble:
This document outlines a transformative business model designed for adaptation, evolution, and seamless integration with AI, AI agents, and social media ecosystems. The core idea — a globally scalable group buying and reverse auction platform — is a flexible foundation for innovation. It can be reimagined as a decentralized commerce engine, a social impact marketplace, or a personalized AI-buyer assistant system. With ongoing advances in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and digital community-building tools, this vision is not only achievable — it is improvable. Future versions may include generative demand creation, autonomous purchasing agents, influencer-led collective negotiations, and automated sustainability scoring — unlocking entirely new dimensions of efficiency, equity, and value.
Executive Summary
Thanks for reading! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
Platform Name: CollectiveBuy Global (Placeholder name )
Vision: To create the world’s premier aggregated purchasing platform that democratizes buying power through intelligent group formation and reverse auction mechanics, enabling consumers globally to access wholesale pricing while providing sellers with predictable demand forecasting and efficient inventory management.
Mission: Revolutionize commerce by connecting buyers and sellers through AI-driven collective purchasing, creating value for all stakeholders while promoting sustainable consumption patterns.
1. Business Vision & Value Proposition
1.1 Core Vision
CollectiveBuy Global will be the world’s first truly global platform combining traditional group buying with innovative reverse auction mechanics, powered by AI and blockchain technology to create transparent, efficient, and equitable commerce for all participants.
- For an outline Software Requirement Document See: Outline SRS
- I was not satisfied with the AI strategy and integration, I created an outline AI strategy consideration paper: Analysis of AI strategy
- Why influencers and social media matter to CollectiveBuy Global and novel buyer and seller white space ideas: Influencer, Social media and White space ideas
These two mechanisms—Group Sales and Reverse Auctions—are mutually reinforcing and foundational to CollectiveBuy Global’s value proposition. Together, they shift pricing power closer to the consumer, while giving sellers a scalable, data-rich model to move inventory strategically and sustainably. Here are precise definitions of Group Sale and Reverse Auction from both the buyer’s and seller’s perspectives within the CollectiveBuy Global platform context:
Group Sale (Group Buying)
For Buyers:
A Group Sale empowers buyers to access significantly reduced prices by forming or joining a group of purchasers interested in the same product. The more people that join the group within a set timeframe, the lower the final price — often unlocking wholesale or bulk discounts that would be otherwise unavailable to individual shoppers.
Buyer Benefits:
- Access to wholesale-like prices
- Real-time discount tracking based on group participation
- Social features for inviting friends or communities
- Lower shipping emissions per unit (eco-friendly)
- Opportunity to support community-driven purchasing
For Sellers:
From the seller’s side, a Group Sale aggregates demand up front. Sellers commit to fulfilling bulk orders once minimum participation is met, allowing them to:
- Predict inventory needs accurately
- Reduce marketing spend due to viral, peer-driven sharing
- Increase average order sizes
- Optimize logistics by consolidating shipments
Seller Advantages:
- Pre-sold volume reduces sales risk
- Data-driven forecasting from real-time group trends
- Reduced customer acquisition costs via community referrals
- Improved warehouse and delivery efficiency
Reverse Auction
For Buyers:
In a Reverse Auction, the buyer specifies the product and the maximum price they are willing to pay. Sellers then compete to offer the best price — ideally driving the final price down. On CollectiveBuy Global, multiple buyers can aggregate their interest to further incentivize sellers.
Buyer Benefits:
- Transparent competition among sellers
- Potential to purchase below retail or even wholesale prices
- AI-supported demand aggregation with similar buyers
- Better matching for niche or custom products
For Sellers:
Sellers view incoming buyer requests and bid to fulfill them by offering their best possible price. It flips traditional sales: instead of setting a price and waiting for buyers, sellers respond to buyer demand.
Seller Advantages:
- Direct access to real-time buyer intent
- Opportunity to liquidate excess stock efficiently
- Competitive intelligence from market bidding behavior
- Lower return rates due to highly targeted demand

1.2 Unique Value Propositions
For Consumers:
- Access to wholesale pricing through collective purchasing power
- Transparent pricing with real-time discount visibility
- AI-powered product discovery and group matching
- Reduced environmental impact through optimized logistics
- Social commerce features fostering community engagement
For Sellers:
- Predictable demand forecasting through pre-orders
- Reduced inventory risk and carrying costs
- Access to global markets without traditional distribution channels
- Dynamic pricing optimization through reverse auctions
- Lower customer acquisition costs through viral group mechanics
For the Platform:
- Revenue from transaction fees, premium services, and data insights
- Network effects creating competitive moats
- Scalable technology infrastructure
- Global market reach with local adaptation
1.3 Novel Features & Innovations
- AI-Powered Group Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms that predict optimal group sizes, pricing, and timing for maximum success rates
- Blockchain-Based Transparency: Smart contracts ensuring fair pricing and automatic discount distribution
- Reverse Auction Aggregation: Buyers specify desired products and prices, sellers compete to fulfil collective demand
- Sustainability Scoring: Carbon footprint tracking and eco-friendly purchasing incentives
- Social Impact Marketplace: Integration with social causes and community development projects
- Dynamic Fulfilment Networks: AI-optimized logistics using local pick-up points and community hubs
2. Market Analysis
2.1 Market Size & Growth
- Global B2C E-commerce Market: $6.2 trillion (2023)
- Group Buying Market: $12.8 billion (2023), CAGR 8.5%
- Reverse Auction Market: $3.2 billion (2023), CAGR 12.3%
- Target Addressable Market: $150 billion by 2030
2.2 Target Segments
Primary Markets:
- Asia-Pacific: Early adopters, high mobile penetration
- Europe: Sustainability-conscious consumers
- North America: Premium product focus
Secondary Markets:
- Latin America: Price-sensitive consumers
- Middle East & Africa: Emerging market opportunities
Customer Personas:
- Value-Conscious Families: Seeking bulk purchases for household items
- Eco-Conscious Millennials: Prioritizing sustainable consumption
- Small Business Owners: Accessing wholesale pricing for inventory
- Community Leaders: Organizing group purchases for neighbourhoods
2.3 Market Trends
- Increasing price sensitivity due to economic uncertainty
- Growing demand for sustainable and ethical consumption
- Rise of social commerce and community-driven purchasing
- Shift towards direct-to-consumer and platform-based retail
3. Competitive Analysis
3.1 Direct Competitors
Pinduoduo (China)
- Strengths: Massive user base, gamification, agricultural focus
- Weaknesses: Limited international presence, quality concerns
- Market Share: 40% of Chinese group buying market
Groupon (Global)
- Strengths: Global presence, established brand, service focus
- Weaknesses: Declining relevance, limited product diversity
- Market Share: 15% of global deals market
Costco/Sam’s Club (Global)
- Strengths: Established wholesale model, brand trust
- Weaknesses: Physical infrastructure requirements, membership fees
- Market Share: 8% of global warehouse club market
3.2 Indirect Competitors
- Amazon Prime (subscription-based discounts)
- Alibaba Group (B2B and B2C platforms)
- Local group buying apps (regional players)
- Traditional wholesale distributors
3.3 Competitive Advantages
- Hybrid Model: Combining group buying with reverse auctions
- Global Reach: Cross-border commerce capabilities
- AI Integration: Advanced algorithms for optimization
- Sustainability Focus: Environmental impact awareness
- Blockchain Transparency: Trust and verification systems
4. Business Model
4.1 Revenue Streams
Primary Revenue (80%):
- Transaction fees: 3-8% of gross merchandise value
- Seller subscription plans: $99-$999/month based on features
- Premium buyer memberships: $49-$149/year for enhanced benefits
Secondary Revenue (20%):
- Advertising and sponsored listings
- Data insights and analytics services
- Logistics and fulfilment services
- White-label platform licensing
4.2 Cost Structure
- Technology development and maintenance (35%)
- Customer acquisition and marketing (25%)
- Operations and customer support (20%)
- Payment processing and transaction costs (10%)
- Administrative and overhead (10%)
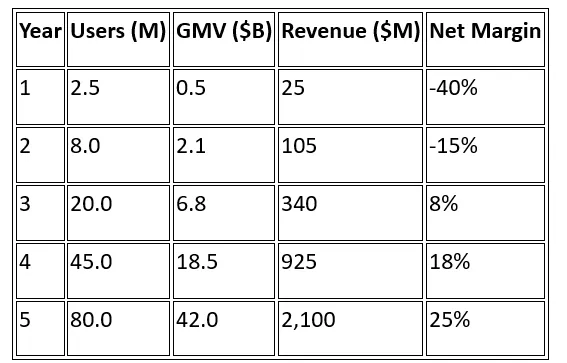
4.3 Financial Projections (5-Year)
5. Technology Architecture
5.1 Core Components
- Group Formation Engine: AI-powered matching and optimization
- Reverse Auction System: Real-time bidding and price discovery
- Blockchain Layer: Smart contracts and transparency
- Mobile-First Platform: Native iOS and Android applications
- Global Logistics Network: Integrated fulfilment solutions
5.2 Technology Stack
- Frontend: React Native, Flutter
- Backend: Node.js, Python, Microservices architecture
- Database: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis
- Cloud: AWS/Azure multi-region deployment
- AI/ML: TensorFlow, PyTorch for recommendation engines
- Blockchain: Ethereum, Polygon for smart contracts
6. SWOT Analysis
6.1 Strengths
- Innovative Business Model: Unique combination of group buying and reverse auctions
- Technology Leadership: Advanced AI and blockchain integration
- Global Scalability: Platform-based model with network effects
- Sustainability Focus: Aligned with consumer trends
- Strong Team: Experienced leadership in e-commerce and technology
6.2 Weaknesses
- Complex Operations: Managing global logistics and multiple stakeholders
- High Capital Requirements: Significant investment needed for global expansion
- Regulatory Complexity: Varying laws across different markets
- Trust Building: Establishing credibility in new markets
- Technical Complexity: Sophisticated platform requiring ongoing development
6.3 Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: High growth potential in developing economies
- B2B Expansion: Extending platform to business customers
- Sustainability Trend: Growing demand for eco-friendly commerce
- Technology Adoption: Increasing comfort with digital platforms
- Economic Pressures: Rising demand for cost-effective purchasing
6.4 Threats
- Intense Competition: Established players with deep pockets
- Economic Downturn: Reduced consumer spending
- Regulatory Changes: Potential restrictions on cross-border commerce
- Technology Risks: Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global logistics challenges
7. PESTLE Analysis
7.1 Political
- Opportunities: Government support for digital commerce and SME development
- Threats: Trade wars, regulatory restrictions, data localization requirements
7.2 Economic
- Opportunities: Economic pressures driving demand for cost savings
- Threats: Recession reducing discretionary spending, currency fluctuations
7.3 Social
- Opportunities: Growing social commerce trends, community-driven purchasing
- Threats: Consumer privacy concerns, digital divide
7.4 Technological
- Opportunities: AI advancement, blockchain adoption, 5G rollout
- Threats: Cybersecurity risks, technology obsolescence
7.5 Legal
- Opportunities: Favourable e-commerce regulations in key markets
- Threats: Consumer protection laws, antitrust concerns
7.6 Environmental
- Opportunities: Sustainability focus, carbon footprint reduction
- Threats: Environmental regulations, packaging restrictions
8. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
8.1 Threat of New Entrants (Medium)
- Barriers: High technology investment, network effects, regulatory compliance
- Enablers: Low physical infrastructure requirements, digital nature
8.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers (Low-Medium)
- Factors: Platform provides access to global markets, multiple seller options
- Considerations: Need to maintain seller satisfaction and competitive pricing
8.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers (Medium)
- Factors: Multiple platform options, price sensitivity
- Mitigation: Unique value proposition, switching costs through community
8.4 Threat of Substitutes (High)
- Alternatives: Traditional e-commerce, physical retail, other group buying platforms
- Differentiation: Unique features, superior pricing, community aspects
8.5 Industry Rivalry (High)
- Factors: Established players, low switching costs, rapid innovation
- Strategy: Focus on differentiation, customer loyalty, operational excellence
9. Risk Analysis & Mitigation
9.1 Strategic Risks
Market Acceptance Risk
- Mitigation: Extensive market research, pilot programs, iterative development
Competition Risk
- Mitigation: Strong IP protection, continuous innovation, strategic partnerships
Technology Risk
- Mitigation: Robust architecture, regular security audits, backup systems
9.2 Operational Risks
Logistics Complexity
- Mitigation: Partner with established logistics providers, local fulfilment centres
Quality Control
- Mitigation: Seller verification systems, customer review mechanisms, return policies
Fraud Prevention
- Mitigation: AI-powered fraud detection, blockchain verification, insurance coverage
9.3 Financial Risks
Cash Flow Management
- Mitigation: Staged funding approach, diverse revenue streams, conservative projections
Currency Risk
- Mitigation: Multi-currency support, hedging strategies, local partnerships
Regulatory Compliance
- Mitigation: Legal expertise in key markets, compliance frameworks, government relations
10. Go-to-Market Strategy
10.1 Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-12)
- Target: 2-3 key markets (Singapore, UK, Canada)
- Focus: Product development, initial seller onboarding
- Investment: $15M for technology and market entry
10.2 Phase 2: Expansion (Months 13-24)
- Target: 8-10 markets across Asia-Pacific and Europe
- Focus: User acquisition, operational scaling
- Investment: $35M for marketing and expansion
10.3 Phase 3: Scale (Months 25-36)
- Target: 20+ markets globally
- Focus: Platform optimization, ecosystem development
- Investment: $75M for global scaling
10.4 Marketing Strategy
- Digital Marketing: SEO, SEM, social media advertising
- Community Building: Influencer partnerships, referral programs
- Strategic Partnerships: Retailers, logistics providers, payment processors
- Content Marketing: Educational content about group buying benefits
11. Critical Success Factors
11.1 Platform Excellence
- User Experience: Intuitive interface, seamless transaction flow
- Technology Performance: Fast loading, reliable operations, mobile optimization
- Trust & Safety: Robust verification, dispute resolution, customer support
11.2 Ecosystem Development
- Seller Network: Diverse, quality suppliers across categories
- User Community: Active, engaged user base with high retention
- Partnership Network: Strategic alliances with logistics, payments, marketing
11.3 Operational Excellence
- Global Operations: Efficient cross-border commerce capabilities
- Customer Service: 24/7 multilingual support, proactive issue resolution
- Data Analytics: Actionable insights driving continuous improvement
12. Critical Analysis & Potential Concerns
12.1 Market Complexity
The global nature of the platform introduces significant complexity in terms of regulatory compliance, cultural adaptation, and operational coordination. Different markets have varying consumer behaviours, legal requirements, and infrastructure capabilities, which could lead to inconsistent user experiences and increased operational costs.
12.2 Technology Challenges
The integration of AI, blockchain, and complex group buying mechanics creates technical risks. The platform must handle high transaction volumes, real-time price calculations, and secure payment processing across multiple currencies and jurisdictions. Any technical failures could severely impact user trust and platform credibility.
12.3 Unit Economics Concerns
The business model depends heavily on achieving scale to justify the high technology and operational costs. The projected path to profitability assumes successful user acquisition and retention, which may prove challenging given the competitive landscape and the complexity of educating consumers about group buying benefits.
12.4 Regulatory Risks
Cross-border commerce faces increasing regulatory scrutiny, particularly around data privacy, taxation, and consumer protection. Changes in international trade policies or platform regulations could significantly impact the business model’s viability.
12.5 Market Saturation
The group buying model has shown mixed results globally, with some markets experiencing fatigue from previous failed platforms. Consumer trust and adoption may be slower than projected, particularly in markets where group buying has negative associations.
13. Conclusion & Recommendations
CollectiveBuy Global represents a significant opportunity to revolutionize global commerce through innovative group buying and reverse auction mechanisms. The platform’s success will depend on:
- Execution Excellence: Flawless technology implementation and user experience
- Market Adaptation: Flexible approach to different regional requirements
- Strategic Partnerships: Strong alliances with key stakeholders
- Financial Discipline: Careful capital allocation and milestone-based funding
- Regulatory Compliance: Proactive approach to legal and regulatory requirements
Recommended Next Steps:
- Conduct detailed market research in target countries
- Develop MVP with core features for pilot testing
- Secure initial funding and assemble core team
- Establish strategic partnerships with logistics and payment providers
- Begin regulatory compliance framework development
The platform has the potential to create significant value for all stakeholders while addressing real consumer needs for cost-effective, sustainable purchasing. However, success will require careful execution, substantial investment, and the ability to navigate complex global market dynamics.
Investment Required: $125M over 36 months Expected ROI: 35-40% by Year 5 Break-even: Month 28 Market Leadership Timeline: 5-7 years
Commentary
CollectiveBuy Global represents more than just a new commerce platform — it is a structural rethinking of how markets function in the digital age. By enabling AI-augmented collective decision-making, algorithmic pricing fairness, and demand-driven logistics, it offers a blueprint for a resilient, inclusive, and intelligent global marketplace. Its adaptability for future AI integration, social commerce dynamics, and sustainability metrics makes it not only viable, but visionary. With focused execution, strong partnerships, and a commitment to continuous learning and improvement, CollectiveBuy Global has the potential to become a market-defining force — one that redefines commerce for a new generation of connected, conscious consumers.



